* Nordic example shown, package may vary by country and region
Fasten the plunger rod into the rubber stopper of the syringe by turning the plugger rod clockwise until it stops.
Remove the blue cap of the powder vial
Penetrate the stopper of the powder vial with the Mini-Spike transfer device
Remove the cap from the syringe and keep it for later use
Hold the syringe upright and carefully press the plunger rod upward to remove air
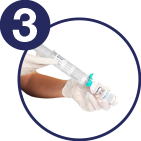
Connect the syringe to the Mini-Spike transfer device
Inject about 10 ml of the solvent into the powder vial
The vial should be about ¾ full
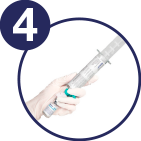
Without withdrawing the Mini-Spike from the vial, hold the powder vial and the syringe in a firm grip
Shake gently to ensure complete dissolution
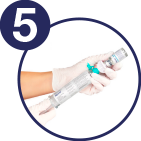
Withdraw all of the dissolved solution from the powder vial into the syringe
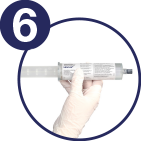
Disconnect the empty vial and Mini-Spike transfer device from the syringe
Plug the syringe with the syringe cap
Gently mix the contents of the syringe
Hexvix is now reconstituted and ready for use
The appearance of the reconstituted solution is clear to slightly opalescent, and colorless to pale yellow

Ensure that the bladder is completely empty prior to Hexvix instillation
Patients should be catheterised
Connect the syringe containing Hexvix to the catheter using
Luer-Lock
Gently instill 50ml of Hexvix into the bladder
Hexvix® reconstitution – additional notes11



Weak fluorescence
- Equipment failure or
- Blood in the bladder or
- Inadequate time or
- Air bubbles or
- Concealed tumours
- Make sure equipment is working and connected properly
- If blood is present, remove resectoscope and flush using a bladder syringe attached to the trocar
- Ensure that Hexvix® was instilled 1 hour prior to cystoscopyr
- Remove any air bubbles
- Look behind any folds
No fluorescence
- The equipment has not been set up correctly or
- Blue Light is not activated
- No malignant activated lesions
- Ensure you are using correct equipment; look for blue or violet marker
- Make sure Hexvix® has been instilled, and check for fluorescence in bladder neck
- Inspect light source; original light bulb?
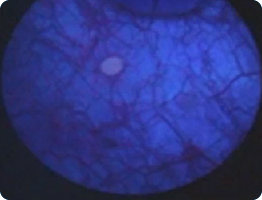
Green hue
- Urine in the bladder
- Always drain the bladder at start of the procedure
- Remove resectoscope, set trocar valve to exit position, and allow urine to drain passively
Entire bladder appears red under white and blue light
- Recent Bacillus Calmette-Guerin treatment or inflammation
- If clinically feasible, avoid BLC® with Hexvix®/Cysview® until 6 weeks after last BCG treatment and in patients with bladder infection
- Either continue procedure without the benefit of Blue Light diagnosis or reschedule
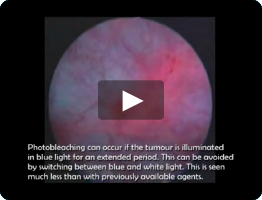
Photo bleaching
- Prolonged use of blue light
- Blue light too close to lesion during procedure
- Alternate between white light and blue light. If the tumour is visible in white light, use BLC® with Hexvix®/Cysview® for control after resection
- Do not use Blue Light close to the tumour for extended time periods. If photo bleaching appears, shut off the blue light and work elsewhere
- Mark small lesions early during procedure
Uncertainty around a large pink/red area
Direct scope 90° toward lesion. Fill bladder slightly. Stretch area with loop and see if it disappears
Questions:
Has a cytology been taken? Were bacterial cultures taken? Has patient used catheter for longer periods?
Is CIS suspected?Cold cup biopsy and no fulguration
Did the patient have a positive urine cytology? Treat as carcinoma in situ
Trouble finding orifice or suspicion that orifice might have been resected
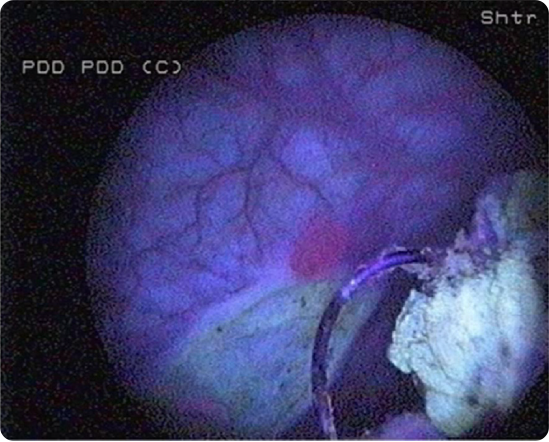
Images courtesy of Professor Malmström, Uppsala University
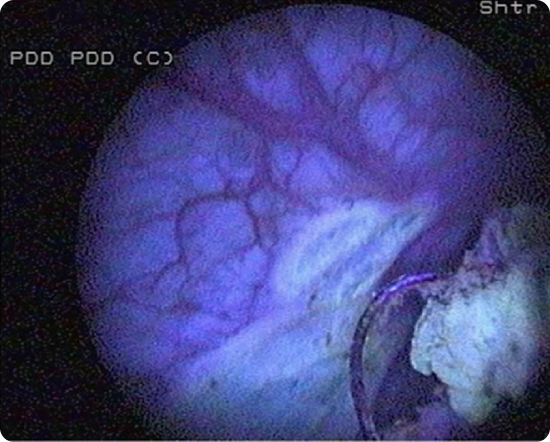
To avoid false-negative diagnoses
Ensure adequate time after instillation of Hexvix®
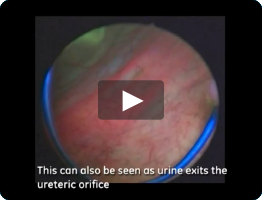
Pink fluorescence on bladder neck should always be seen if the instillation was administered properly
Images courtesy of Dr. Sia Daneshmand, Keck Hospital, USC
Bladder neck
Fluorescence is considered normal and not necessarily tumour
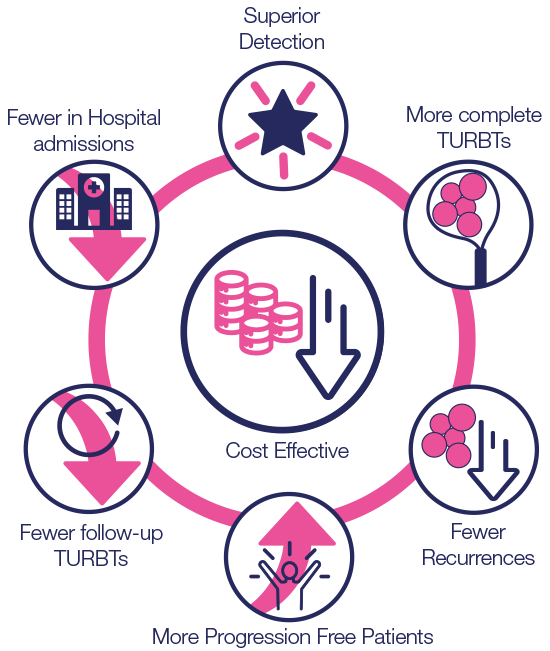
Hexvix® is cost effective in the treatment and management of NMIBC8,22
- Hexvix® and single shot mitomycin (MMC) led to a reduction in the number of TURBTs and patients requiring in-hospital admission compared to WLC27
- Reduction in the cost burden of NMIBC in terms of further management (follow-up repeated TURBTs) and treatment (chemotherapy instillation, BCG instillation, cystectomy)8
- Bladder cancer has the highest lifetime treatment cost per patient of all cancers24,25,26
- Use local Budget Impact Models, Value Dossiers and other Health Economics tools as appropriate references when creating your health economics messaging for your market
- The key is to highlight the core items in the diagram opposite “Hexvix® reduces the cost burden of bladder cancer treatment versus WLC alone8
The use of Hexvix® to assist primary TURBT is more expensive than WLC alone
- Hexvix® combined with single shot mitomycin (MMC) led to a reduction in the number of TURBTs and patients requiring in-hospital admission compared to WLC27
- Reduction in the cost burden of NMIBC in terms of further management (follow-up repeated TURBTs) and treatment (chemotherapy instillation, BCG instillation, cystectomy)8
- Bladder cancer has the highest lifetime treatment cost per patient of all cancers26
Hexvix® use led to reduced healthcare costs8
When should I use Hexvix®
All major international NMIBC guidelines contain guidance on Hexvix® use and should be consulted16-28
Hexvix® use is covered in AUA, EAU, NCCN, NICE, AFU, and amongst other major international and national NMIBC guidelines
Hexvix® should be used for the first TURBT and for all intermediate and high-risk patients, during surgical treatment and surveillance/follow-up2,8,9
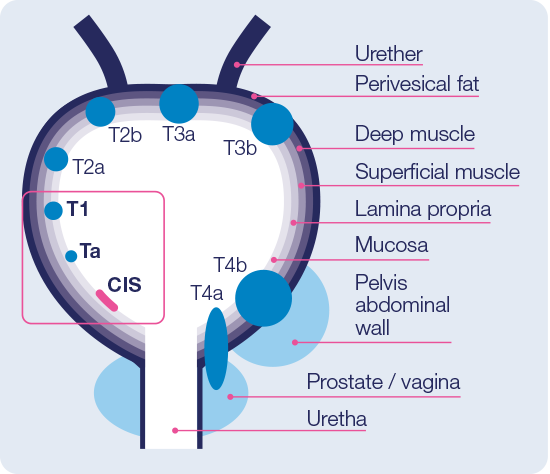
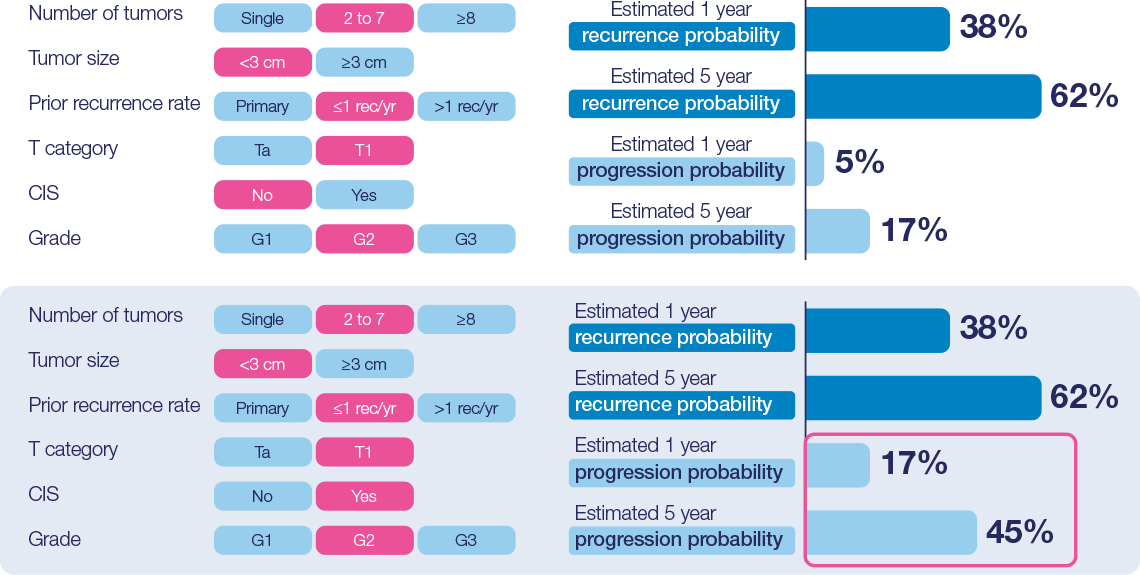
EORTC risk categories - basis for stratification of treatment and follow-up14
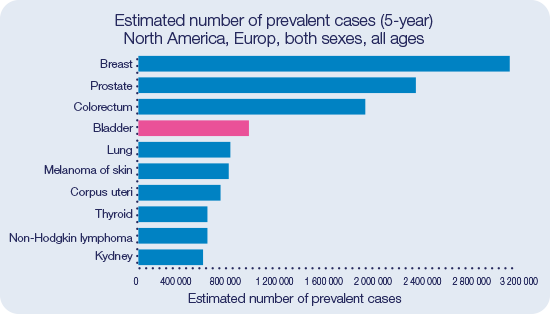
Bladder Cancer is the fourth most prevalent cancer for both sexes in Europe and North America.29
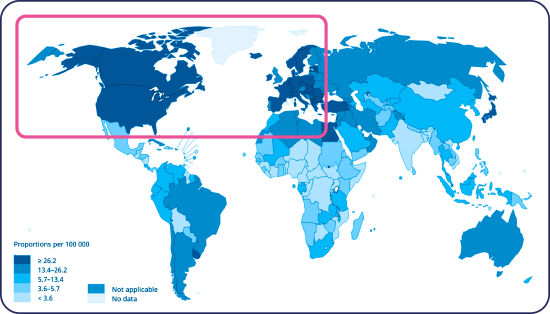
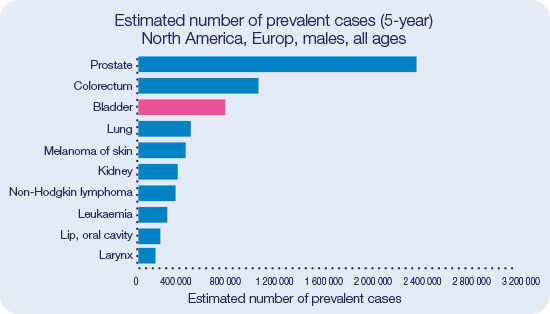
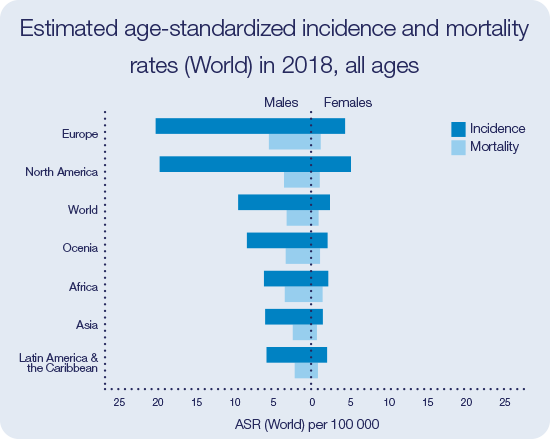
Incidence and mortality of bladder cancer is particularly high in Europe and North America32
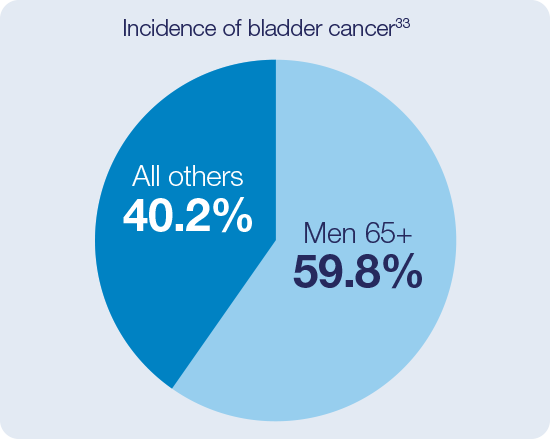
High rate of incomplete TURBTs
High rate of residual tumor after Transurethral Resection of Bladder Tumor (TURBT), 34% - 76% of patients have evidence of
tumor on repeat TURBT at 2-6 weeks35,36,37
Comparatively little evolution in the 5-year relative survival rate for Bladder cancer versus other cancers since 197538
High recurrence rate and risk of progression requires frequent and
lifetime follow-up with:
- Multiple cystoscopies
- TURBTs
- Instillation therapy
- For more information please refer to the Patient Burden Section