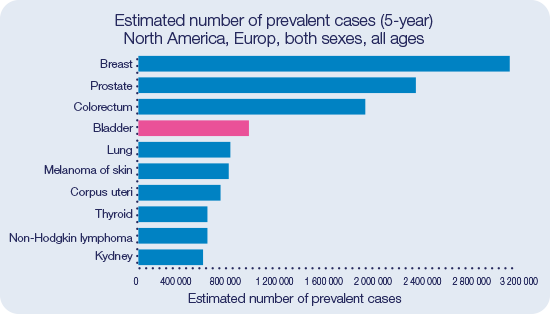
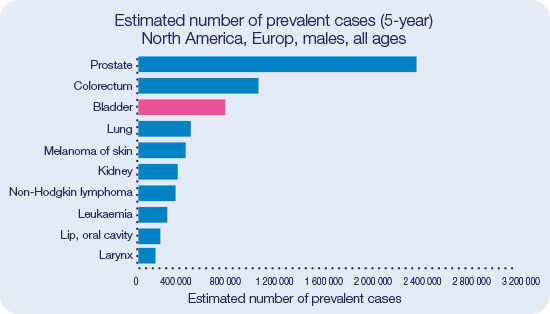
Bladder Cancer is the fourth most prevalent cancer for both sexes in Europe and North America.29
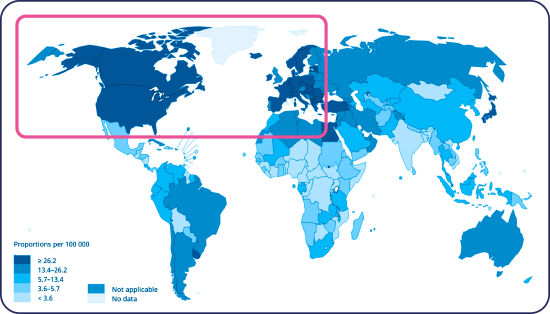
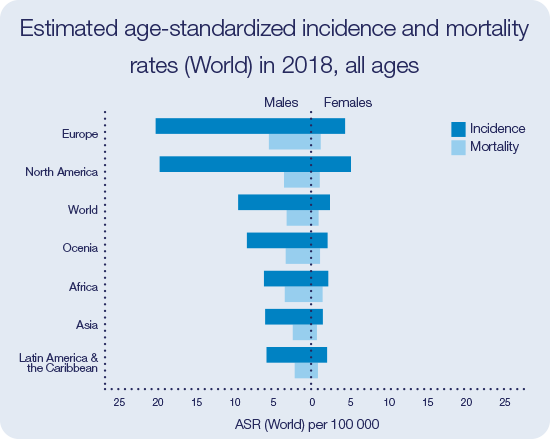
Incidence and mortality of bladder cancer is particularly high in Europe and North America32
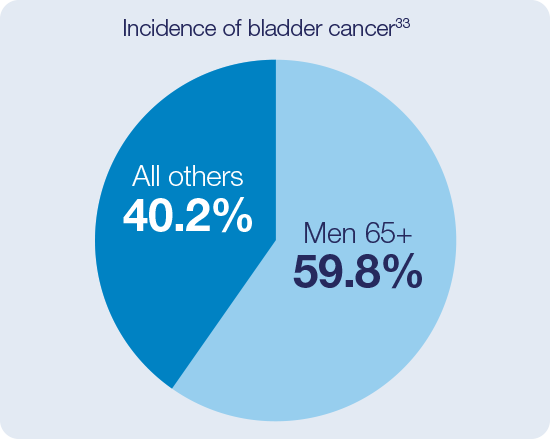
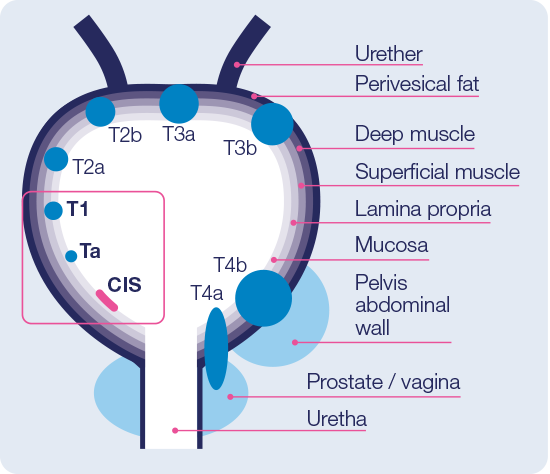
- Non-muscular invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) includes the subtypes:

- Approximately 75% of patients with BC present with a disease confined to the mucosa (stage Ta, CIS) or submucosa (stage T1)16
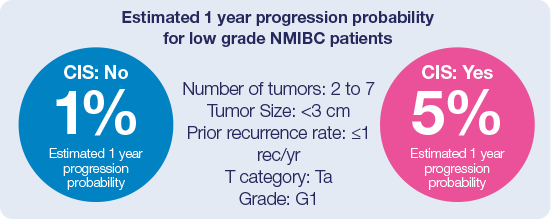
- T1 and CIS, as compared to Ta, have high malignant potential16
- CIS is the hardest of all tumors to detect13
High rate of incomplete TURBTs
High rate of residual tumor after Transurethral Resection of Bladder Tumor (TURBT), 34% - 76% of patients have evidence of
tumor on repeat TURBT at 2-6 weeks35,36,37
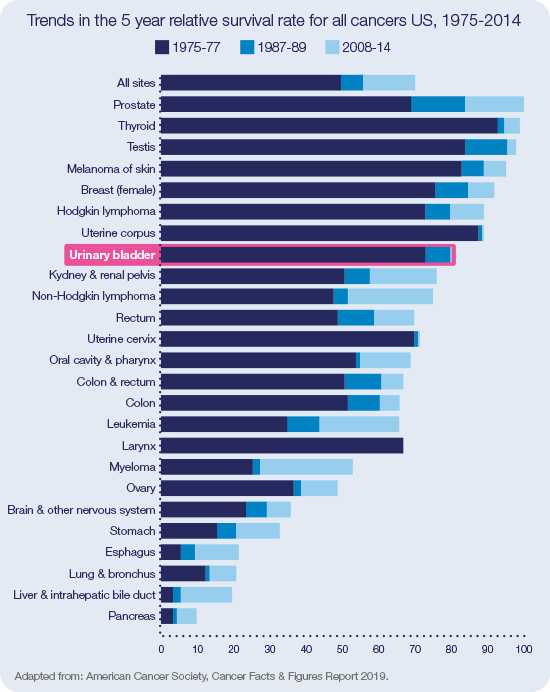
Comparatively little evolution in the 5-year relative survival rate for Bladder cancer versus other cancers since 197538
High recurrence rate and risk of progression requires frequent and
lifetime follow-up with:
- Multiple cystoscopies
- TURBTs
- Instillation therapy
For more information please refer to the Patient Burden Section